The most fundamental data structure is an array. An array is a collection of data that can be accessed by indexing. Depending on the language, an array may hold a single type of data or a collection of different types of data.
Array Implementation
Let's take a look at how we can create an array, declare a size, and add data.
Creating an Array
Creating an array is as simple as declaring a variable and assigning it a value. Let's take a look at creating an array Java, JavaScript, and C#.
Java
int myArray[];
JavaScript
let myArray = [];
C#
int[] myArray;
In each of these declarations, we are not adding any data. We are simply initializing the array.
Exercise
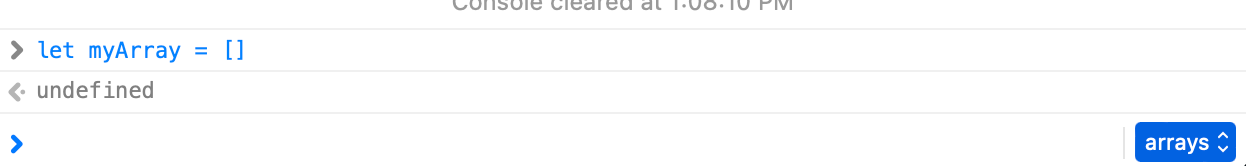
Open your developer tools and create a JavaScript array called myArray. We can do this by writing let myArray = [] in the console.
Declaring an Array Size
Now that we have an array, we can initialize the size.
Java
myArray = new int[5];
JavaScript
myArray = new Array(5);
C#
myArray = new int[5];
Adding Data
Now that we have an array and it's size declared, we can add data to the array. We can add data in multiple ways. The most common way is adding it all at once, or by adding it via an index.
Java, JavaScript, and C#
We can add data via indexing the same way in all 3 languages.
myArray[0] = 1;
myArray[1] = 2;
myArray[2] = 3;
myArray[3] = 4;
myArray[4] = 5;
Doing it All at Once
Creating an array, declaring a size, and adding data in 3 seperate steps is the long way of doing it. We can do it all at once in one line.
Java
int[] myArray = new int[]{ 10, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
JavaScript
let myArray = [10, 3, 5, 7, 9]; // no need to declare types in JS!
C#
int[] myArray = new int[] { 10, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
In Java and C#, all items in the array must be of the same type; in this case int. In JavaScript, we can mix and match types.
let myArray = [3.14, "Ben", true, false, null];
Accessing Array Data
Now that the array is made, we can access the data in the array. We can access data the same way we added it.
Java
System.out.println(myArray[0]);
JavaScript
console.log(myArray[0]);
C#
Console.WriteLine(myArray[0]);
Accessing all data in an Array
Unfortunately, we cannot access all data in an array by printing out the entire array like this: System.out.println(myArray). We need to instead, loop over the array and print out each item.
We can follow the folling steps to print out all data in an array:
- Loop over each element in the array.
- Print out the element.
We can use for loops to loop over an array and length to get the length of the array.
Java
for(int i = 0; i < myArray.length; i++) {
System.out.println(myArray[i]);
}
JavaScript
for(let i = 0; i < myArray.length; i++) {
console.log(myArray[i]);
}
C#
for(int i = 0; i < myArray.Length; i++) {
Console.WriteLine(myArray[i]);
}
Multi Dimensional Arrays - Matrix
We can also create and access data in a multi dimensional array. This is useful for creating a matrix or a grid or some sort.
Java
int[][] myMatrix = new int[3][3]; // Declare a 3x3 matrix
myMatrix[0][0] = 1; // Set the first element in the first row to 1
System.out.println(myMatrix[0][0]); // Print out the first element in the first row
int[][] myMatrix = new int[][] { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } }; // Declare a 3x3 matrix and add data in one line
JavaScript
let myMatrix = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ]; // Declare a 3x3 matrix and add data in one line
console.log(myMatrix[0][0]); // Print out the first element in the first row
C#
int[][] myMatrix = new int[][] { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } }; // Declare a 3x3 matrix and add data in one line
Console.WriteLine(myMatrix[0][0]); // Print out the first element in the first row
Accessing All Data
To access all the data in the matrix, we need to use a nested loop.
Java
for(int i = 0; i < myMatrix.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < myMatrix[i].length; j++) {
System.out.println(myMatrix[i][j]);
}
}
JavaScript
for(let i = 0; i < myMatrix.length; i++) {
for(let j = 0; j < myMatrix[i].length; j++) {
console.log(myMatrix[i][j]);
}
}
C#
for(int i = 0; i < myMatrix.Length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < myMatrix[i].Length; j++) {
Console.WriteLine(myMatrix[i][j]);
}
}
Conclusion
That's it for arrays. In the algorithms course we will learn how to do all sorts of things with arrays. To recap, in this module we learned how to create arrays, declare the size of the array, and add data to the array. We also learned how to access data in an array by indexing and looping over the array.